
Virtual Reality in Medicine – The Current Reality and Exciting Prospects
Modern medicine is evolving rapidly, and one of the most advanced technologies being actively implemented in clinical practice and education is Virtual Reality (VR). The use of VR in medicine allows for simulating complex surgical procedures, training professionals without risking patient safety, and providing realistic simulations for rehabilitation, diagnostics, and therapy.
In this article, we will explore in detail how VR technologies in medicine are transforming treatment approaches, what benefits they offer, and what future prospects lie ahead for this growing field.
How VR Simulates the Real Medical World
VR in medicine is not just a technology—it’s a new paradigm in learning and treatment. With the help of specialized devices and software solutions, it is possible to create three-dimensional models of organs, conduct virtual surgeries, train actions in critical situations, and even diagnose mental disorders.
Simulation Examples in VR:
- Training surgical procedures without a real patient
- Conducting virtual examinations
- Simulating childbirth and emergency care
- Testing cognitive and motor functions
Practical Examples of Using Virtual Reality
1. Education and Training of Professionals
- VR in medicine allows future doctors and nurses to practice skills in environments as close to reality as possible.
- Surgical operation simulations boost confidence and reduce student stress.
- Using 3D models helps better understand human anatomy.
2. Psychotherapy and Neurorehabilitation
- Virtual environments are used in the treatment of phobias, PTSD, and anxiety.
- Patients can interact with simulated situations and gradually overcome fears.
3. Physical Rehabilitation
- VR technologies are applied in motor recovery after strokes and injuries.
- Technology allows for modeling training exercises and tracking patient progress.
4. Palliative and Pain Management
- Immersive VR programs reduce pain in cancer and seriously ill patients.
- VR distraction decreases the need for analgesics.
5. Diagnostics and Preoperative Planning
- Doctors can create 3D models of organs for a specific patient before surgery.
- This improves surgical planning and reduces risks.
Benefits and Applications of VR in Medicine
| Benefit | Description |
| Safe Learning | Ability to train without risk to real patients |
| Personalized Approach | Content can be customized for each individual patient |
| Cost and Time Efficiency | Reduced need for materials, instructors, and rental spaces |
| High Realism | Interactive simulations closely mimic reality |
| Progress Tracking | Automated data collection and analysis of user actions |
| Increased Engagement | Immersion boosts motivation in both patients and students |
Technology Implementation: How It Works
For effective implementation of VR technologies in medicine, the following components are used:
- VR Headsets: Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, Pico, and others
- Specialized Software: Touch Surgery, Osso VR, Medical Realities
- Interactive Interfaces: haptic gloves, motion tracking devices
- Server Solutions and Cloud Storage: for collaborative work with data
Chart: Global VR in Healthcare Market Growth (2020–2030)
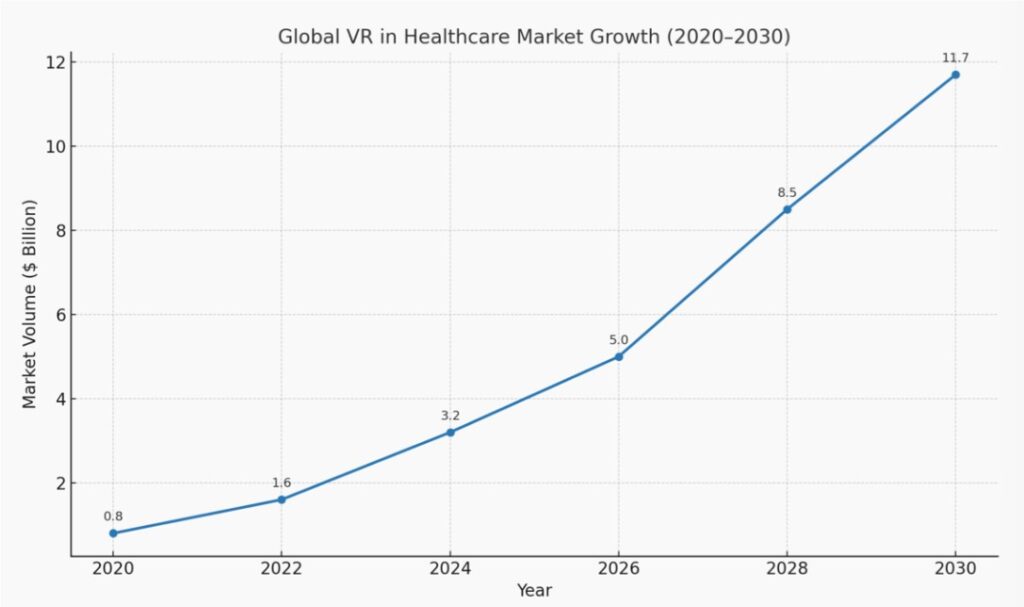
Future Prospects of Using VR
According to research agencies, the VR healthcare market is expected to grow by 25–30% annually. Key development directions include:
- Integration with AI: virtual assistants and personalized treatment recommendations
- Virtual Operating Rooms: collaborative surgery by doctors from different countries
- Therapy with Neurointerfaces
- Cloud VR Platforms: for global medical training
- Expanded Use in Telemedicine
Anticipated Changes:
- Greater accessibility to quality medical education
- Wide implementation in private clinics and public institutions
- Development of new treatment protocols with virtual simulation components
Comparison: VR vs. Traditional Training and Treatment Methods
| Parameter | Traditional Approach | VR Approach |
| Safety | Risk of mistakes on real patients | Completely safe modeling |
| Training Cost | High | Lower in the long term |
| Accessibility | Requires physical presence | Remote learning possible |
| Learning Speed | Slow | Fast due to repetition and interactivity |
| Patient Customization | Limited | Full personalization based on individual parameters |
Conclusion
The application of virtual reality in medicine is not just a trend—it is a powerful tool transforming treatment and education at their core. VR enables doctors and patients to reach a new level of interaction and opens up possibilities that once seemed like science fiction.
The future of medicine lies in simulation, education, treatment, and rehabilitation that occur in virtual environments. The earlier this transformation begins, the greater its impact will be.
VR technologies in medicine represent a synthesis of precision, efficiency, and humanity.
